Introduction
A recent psychology study investigated how caffeine affects people when they are under pressure to perform. While caffeine is commonly known for increasing alertness, researchers wanted to understand whether it also influences motivation, specifically whether people persist longer on difficult tasks during stressful situations.
Conceptual Infographic
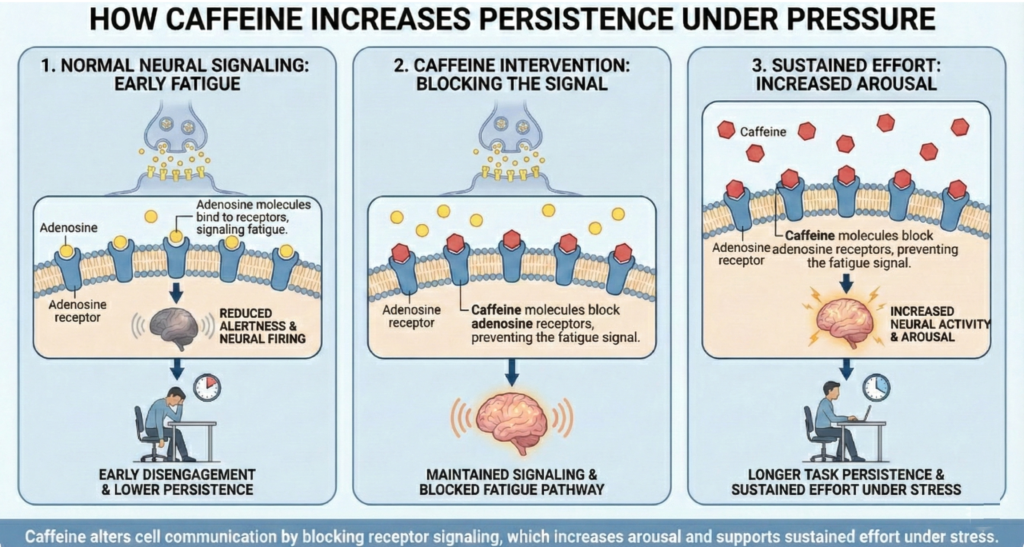
Methods
Participants were asked to complete challenging tasks designed to create time pressure and performance stress. One group consumed caffeine before starting the task, while a comparison group did not. Researchers measured how long participants continued working, how likely they were to disengage, and how their effort changed as the task became more demanding.
Results
Participants who consumed caffeine showed greater task persistence under pressure. They were more likely to continue working on difficult tasks rather than quitting early. Caffeine did not significantly improve accuracy or skill level, but it increased the amount of effort participants were willing to sustain when the task became stressful.
Data Visualization
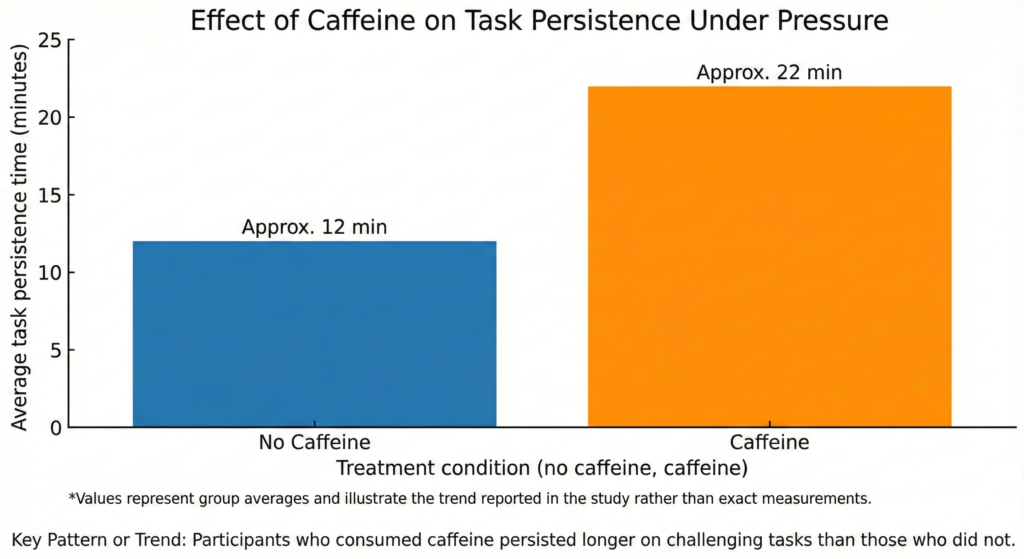
Discussion
The findings suggest that caffeine primarily affects motivation and physiological arousal rather than task ability. By altering neural signaling related to alertness and stress tolerance, caffeine helps individuals remain engaged during demanding situations. This helps explain why caffeine is widely used in academic, athletic, and high pressure environments, although increased persistence does not always guarantee better performance outcomes.
Key Vocabulary and Definitions
Task persistence: The tendency to continue working on a task despite difficulty or pressure.
Psychological stress: A mental state triggered by demanding or high pressure situations.
Arousal: A physiological state of increased alertness and responsiveness.
Chemical signaling: Communication between cells using molecules that bind to specific receptors.
Curriculum Connections
Learning Objectives
- 4.1.A Describe the mechanisms of cell communication.
- 4.2.A Explain how signal transduction pathways regulate cellular processes.
- 8.1.A Explain how environmental factors affect organism behavior.
Essential Knowledge
- 4.1.A.1 Cell signaling evolved early in the history of life.
- 4.2.B.1 Signal transduction pathways link signal reception with cellular responses.
- 4.2.B.2 Signaling cascades relay signals from receptors to cell targets.
- 8.1.A.1 Organisms respond to environmental stimuli through behaviors that increase survival and reproduction.


