Introduction
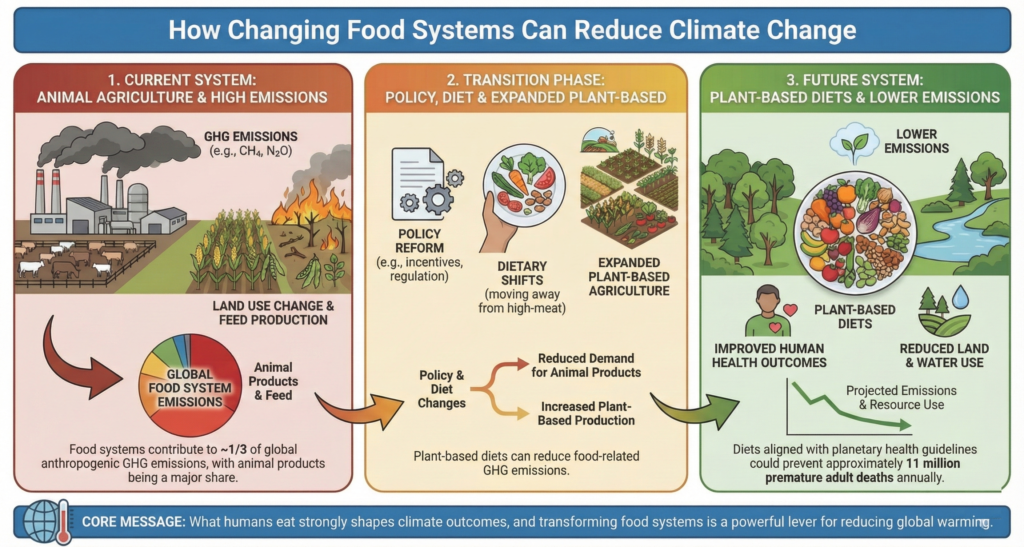
Researchers writing in Oxford Open Climate Change, a peer-reviewed journal from Oxford University Press, examined how the global food system contributes to climate change and evaluated whether shifting toward plant-based diets could meaningfully reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The authors argue that food production, particularly intensive animal agriculture, has been underemphasized in climate solutions despite its large environmental impact.
Conceptual Infographic
Methods
The authors synthesized data from climate models, agricultural emission inventories, and dietary scenario analyses. They compared projected greenhouse gas emissions under current global dietary patterns with scenarios that involve a widespread transition toward predominantly plant-based diets. Their analysis also incorporated evidence related to land use, water use, human health outcomes, and economic effects associated with different food system pathways.
Results
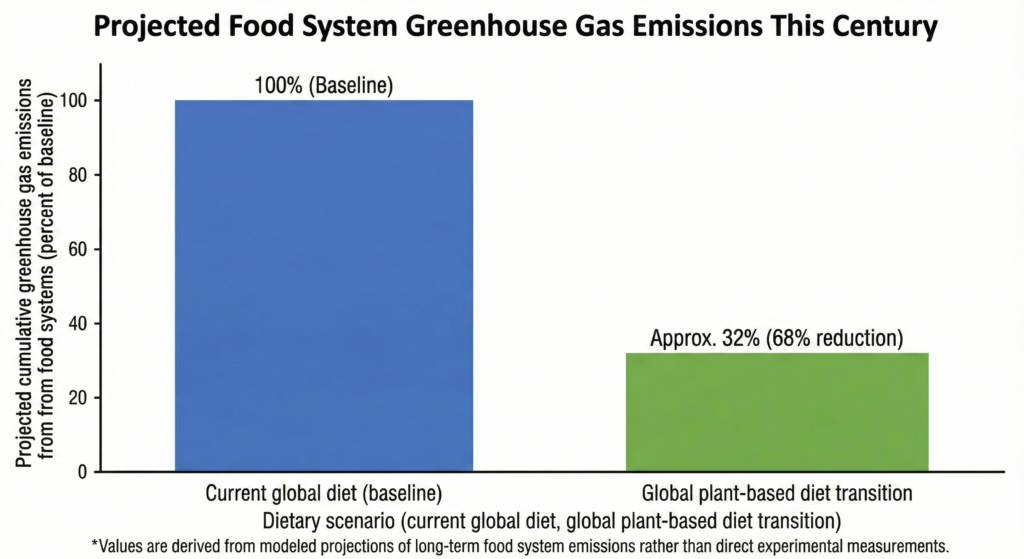
The analysis indicates that a global transition toward plant-based diets could reduce food-system-related greenhouse gas emissions by approximately 68 percent over this century. Animal agriculture was identified as a major emissions source due to methane production, land conversion, and inefficient energy transfer between trophic levels. The authors also report that plant-based food systems could support improved public health, reduce healthcare costs, conserve freshwater resources, and allow more people to be fed using less land.
Data Visualization
Discussion
The authors conclude that transforming food systems is one of the most powerful and underused strategies for climate mitigation. Reducing reliance on intensive animal agriculture while expanding plant-based food production could significantly slow climate change and increase ecosystem stability. While cultural, economic, and political challenges remain, the authors emphasize that coordinated policy changes, incentives, and public education could enable a fair and effective transition.
Key Vocabulary and Definitions
Plant-based diet: A diet that emphasizes foods derived from plants and minimizes or excludes animal products.
Animal agriculture: The farming of animals for food, including meat, dairy, and eggs.
Greenhouse gas emissions: Gases released into the atmosphere that trap heat and contribute to global warming.
Climate mitigation: Actions taken to reduce the causes or severity of climate change.
Curriculum Connections
Learning Objectives
- 8.2.B Describe the role of energy transfer in an ecosystem.
- 8.7.C Explain how human activities affect ecosystem dynamics.
Essential Knowledge
- 8.2.B.2 Energy is transferred through food webs in ecosystems.
- 8.2.C.2 The amount of energy available decreases at each trophic level.
- 8.7.C.1 Human activities can disrupt ecosystems and affect biodiversity.

